
FAQ Topic
Why is Tongue Thrust Important?
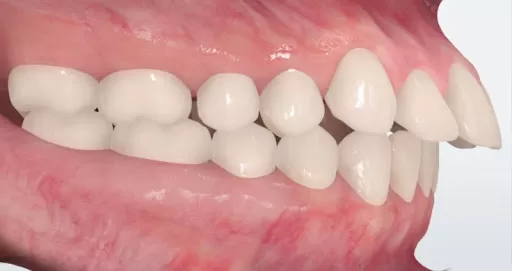 During proper swallowing mechanics, the tongue produces a wave to move the bolus (a bite of food that's been chewed and is ready for digestion) down the esophagus and into the stomach.
During proper swallowing mechanics, the tongue produces a wave to move the bolus (a bite of food that's been chewed and is ready for digestion) down the esophagus and into the stomach.When the tongue thrusts forward during swallowing, this can result in an anterior open-bite where the top and bottom front teeth do not bite together fully. The tongue can also thrust posteriorly or laterally. This can result in an open-bite or cross-bite at the back teeth, and often contributes to a deep overbite of the front teeth.
This phenomenon is considered a retained infantile swallowing pattern, since the "suck-swallow-breathe" pattern during infant breast-feeding is still observed despite the introduction of solid food. Improper swallowing mechanics are often a result of other orofacial dysfunction, such as low tongue and mouth-breathing.
Many people with a tongue-thrust struggle to maintain their airway during dental appointments, especially with cavitron use during a dental cleaning (like water-pooling at the back of the throat), rubber dams, and a "strong tongue or lip" that tends to push dental tools in the mouth away.
